General
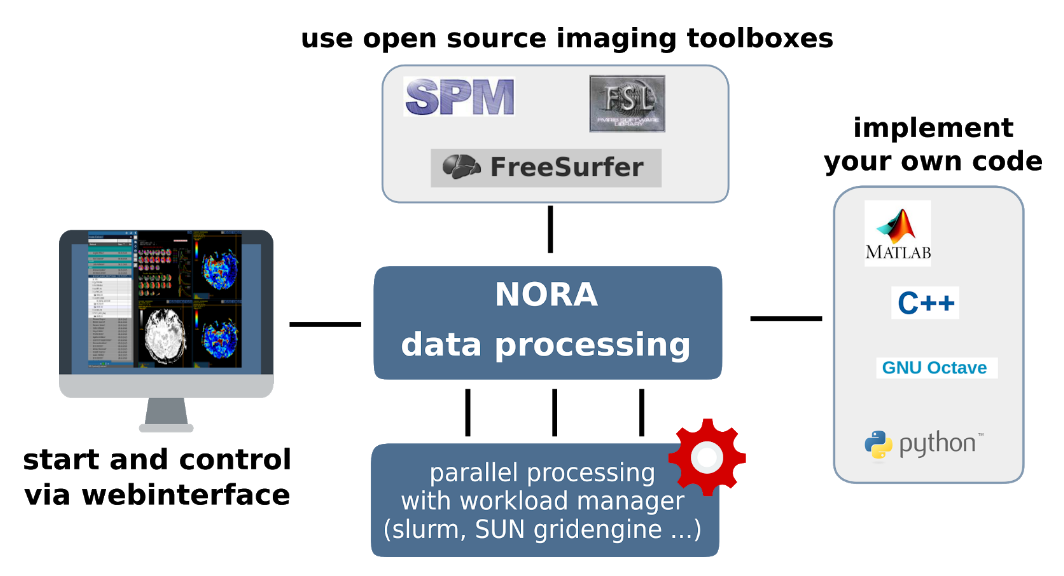
The batchtool was created out of the needs to apply common neuroimaging pipelines (like SPM, FSL, Freesurfer) on medium sized projects (10-1000 subjects) in a convenient and efficient manner. One of the major objective of NORA's batchtool is to deal with heterogenous data. Typically files (a.k.a. image series) are selected by file patterns, which can iteratively generalized. Errors can be easily tracked by a simple error logging system. For example, it is simple to select a errornous subgroup and rerun a modified job for them, which was corrected for the error. Processing pipelines (batches) are a simple linear series of jobs. Depending on the relationship between individual jobs, they can run serially or in parallel.
In conclusion, what it provides:
- Convenient selection of subject/study sets to apply certain processing pipelines
- Definitions of inputs via Tags or filepatterns with wildcards
- Composition of processing pipelines based on predefined scripts/jobs (mostly MATLAB), or custom MATLAB/BASH/Python code
- Submission of jobs to a cluster (Slurm/SGE) with direct access to logs and errors
The Batchtool Window
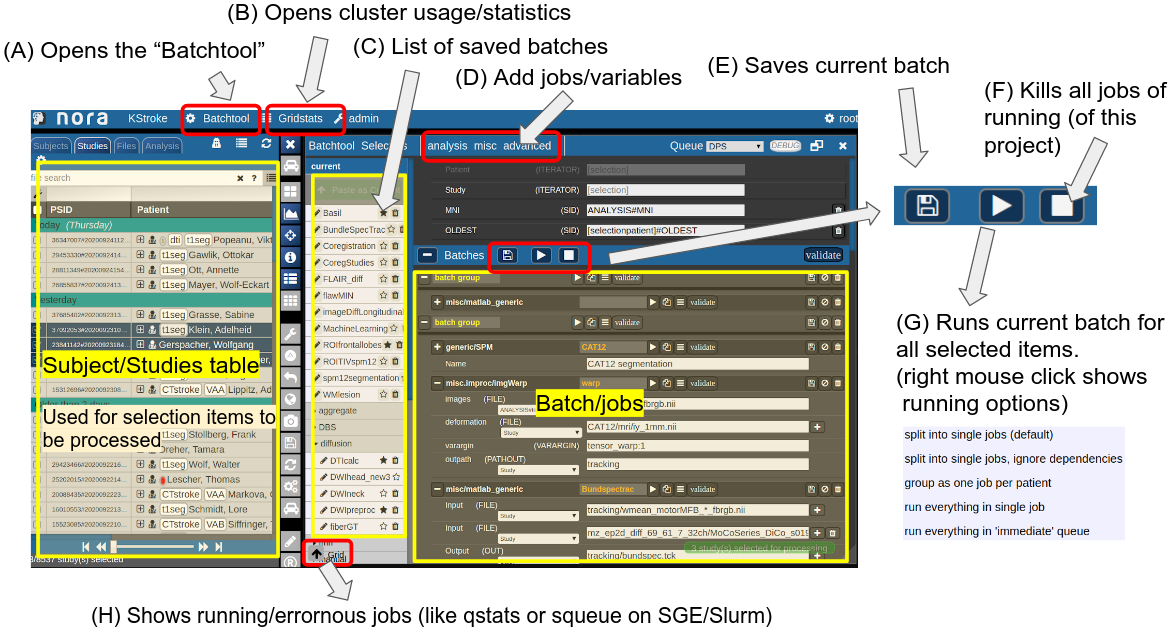
The subject/studies table on the left is used for the selection of subject/studies on which you want to run your batch. You can use the filter bars to create the subgroup you want to work on (see Subject/Studies table). Select on "Batchtool" on the top toolbar (A) to open the batchtool. Below you see the structure of the Bacthtool window. It allows to compose the batch out of single jobs. Jobs are added from the menu (D). You can save batches (E), which then appear in the batch list (C). To open an overview of currently running jobs open the "Gridstats" window (B) or (H).
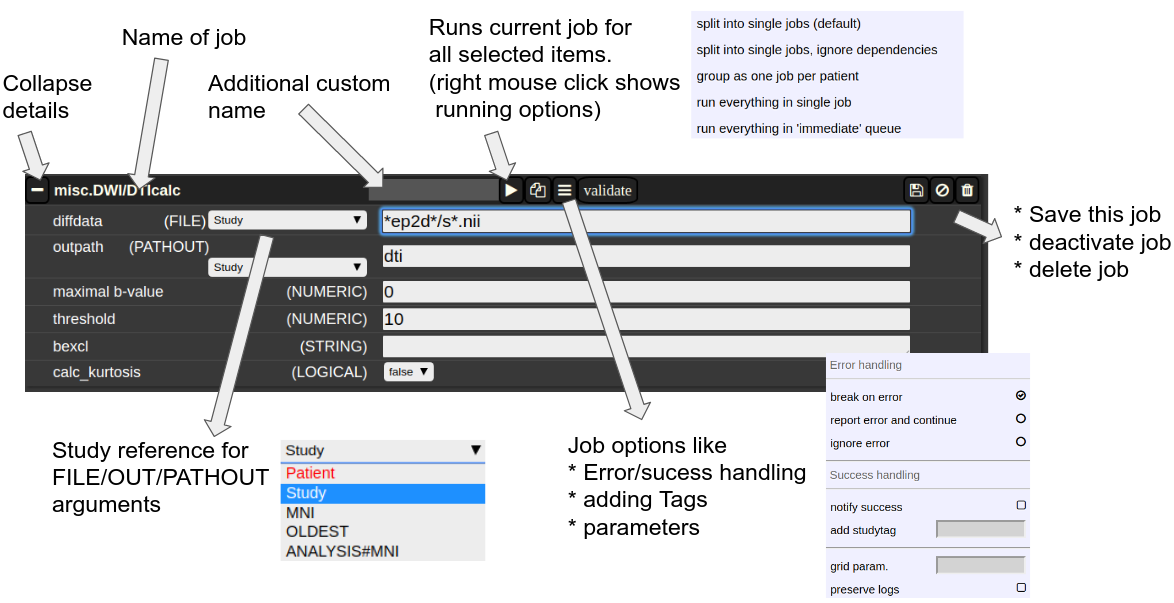
The Anatomy of a Job
A job consists of a list of arguments. There are several types of arguments:
- FILE
All input images/series are given as FILE arguments. Usually you give a FILE pattern instead of an explicit filename. A FIle pattern is a combination of subfolders and filename and wildcards. For example: subfolder1/subf*/s0__.nii. It can contains asterisks (*) as a placeholder for an arbitrary chrceter sequence, or a underscore "_" for a singl characeter placeholder. Internally, the wildcards are the same as for SQL "like" statement (the '*' is replaced by '%'). - OUT
- PATHOUT
- NUMERIC
- STRING
- LOGICAL
- OPTION